How to support (Long Term) Motivation in Cardiac Telerehabilitation Patients: Guidelines based on Interviews and a Narrative Literature Review – 1st year Master 2020
Aim: Find an answer to the question “What are design guidelines that are interesting for telerehabilitation platform design to use, that potentially help to motivate cardiac patients during telerehabilitation?”
Theme: Telerehabilitation; cardiology; motivation; design guidelines.
Cardiovascular disease continues to be a major cause of morbidity worldwide, and is accounting for approximately 40,000 annual deaths in the Netherlands alone [1]. The medical benefits of participating in a rehabilitation program for cardiac patients have been proven. However long-term clinical effectiveness is often poor because of patients’ lack of participation in rehabilitation activities [2].
Telerehabilitation seems to be a promising upcoming alternative to in-hospital rehabilitation with many benefits for patient and hospital alike. But telerehabilitation is still in its starting phase and not yet widely used. Many questions about the use of telerehabilitation remain unanswered. Amongst which how to create this motivation for a patient to finish the rehabilitation program and keep the healthy lifestyle the rehabilitation program advices.
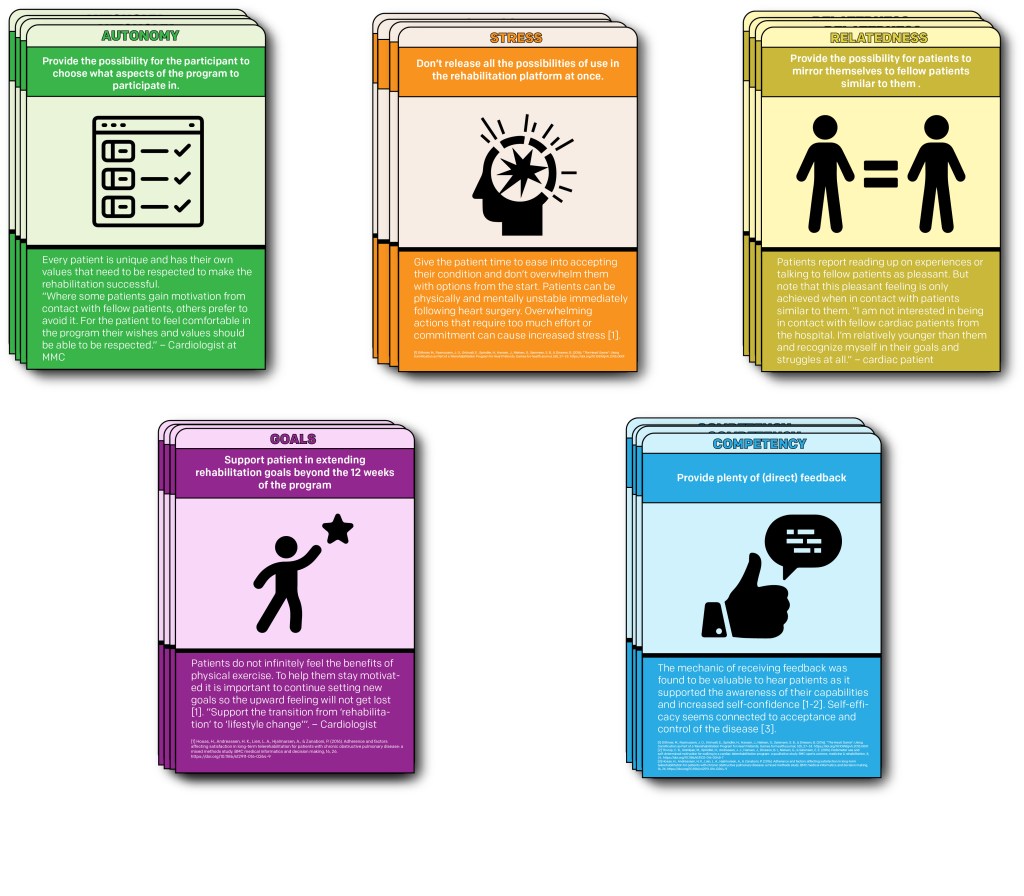
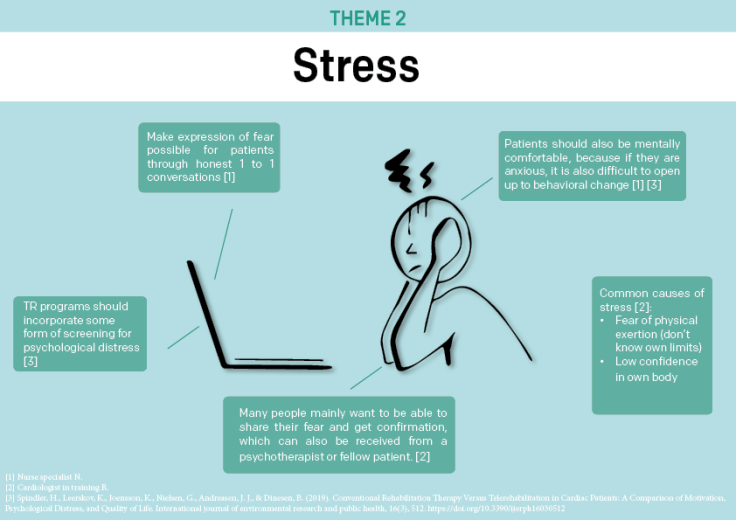
I did a multi-perspective analysis on the topic of (long term) motivation in cardiac telerehabilitation patients. By doing a narrative literature review to gain insights into how (long term) motivation was successfully obtained or how it failed to be obtained in original research papers. I have categorized these insights into themes. Based on these determined themes I conducted semi-structured interviews with cardiac telerehabilitation experts; a cardiologist, nurse specialist and a cardiac patient. To evaluate and enrich the insights from the literature review.
From this analysis I formulated a list of design recommendations for designers to stimulate (long-term) motivation for their platform users. These recommendations will be assessed on clarity and value by designers working in the cardiac or telerehabilitation field.
By formulating these guidelines I want to contribute to the effectiveness of cardiac tele-rehabilitation for patients.
[1] Vaartjes, I., Van Dis, I., Visseren, F. L. J., & Bots, M. L. (2013). Hart-en vaatziekten in Nederland 2013, cijfers over leefstijl, risicofactoren, ziekte en sterfte. Den Haag: Hartstichting, 2941-2947.)
[2] Frederix, I., Vanhees, L., Dendale, P., & Goetschalckx, K. (2015). A review of telerehabilitation for cardiac patients. Journal of telemedicine and telecare, 21(1), 45–53. https://doi.org/10.1177/1357633X14562732






Leave a comment